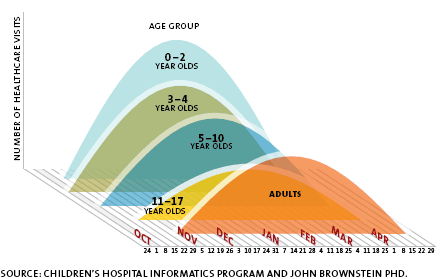
A sophisticated biosurveillance network called the Automated Epidemiologic Geotemporal Integrated Surveillance system (AEGIS), designed to detect the spread of regional epidemics and bioterrorism, has shed new light on how the flu is spread. The system, designed by the Children’s Hospital Boston, collects data from emergency rooms in eight Boston-area hospitals, tracks symptoms and compares them to historical trends in real time. When an anomaly appears, an alert is sent to the Massachusetts Department of Public Health. The graphic below shows that when it comes to spreading flu, preschoolers excel early and often.
Get the free newsletter
Subscribe to Daily Tech Insider for top news, trends, and analysis.
Previous article
Next article
CIO Insight offers thought leadership and best practices in the IT security and management industry while providing expert recommendations on software solutions for IT leaders. It is the trusted resource for security professionals who need network monitoring technology and solutions to maintain regulatory compliance for their teams and organizations.