
Best Security Approach: Layers and Trained Staff
 Best Security Approach: Layers and Trained Staff
Best Security Approach: Layers and Trained Staff
People are a key part of any security program, which includes hiring and retaining skilled security pros and using technology to maximize their effectiveness.
 Phishing Attacks Worldwide
Phishing Attacks Worldwide
Phishing attacks were responsible for 73% of malware delivered to organizations. Nearly 30% of attacks detected worldwide targeted end-user technologies, including Adobe products, Java and Internet Explorer.
 Technologies Most Targeted on Users’ Computers
Technologies Most Targeted on Users’ Computers
The three technologies on end-user computers that were targeted the most were Adobe Flash Player, Microsoft Internet Explorer and Microsoft Silverlight.
 Steady Decline in Exploit Kit Activity
Steady Decline in Exploit Kit Activity
13% of exploit kit activity occurred during the third quarter of 2016, reflecting a steady decline in such activity throughout that year.
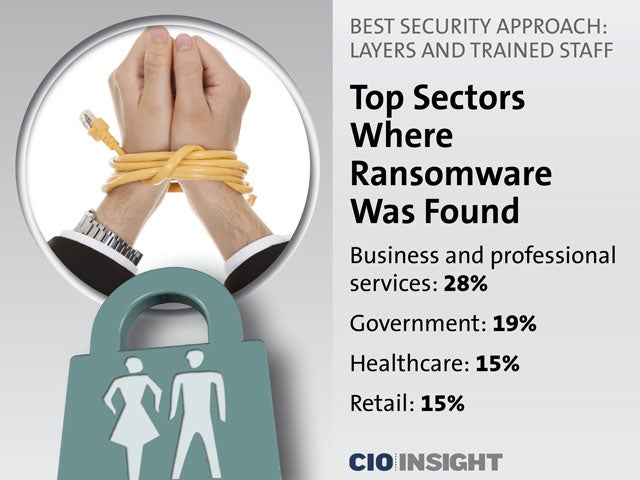 Top Sectors Where Ransomware Was Found
Top Sectors Where Ransomware Was Found
Business and professional services: 28%,
Government: 19%,
Healthcare: 15%,
Retail: 15%
 Finance Industry Under Fire Everywhere
Finance Industry Under Fire Everywhere
The finance industry was the only one to appear in the top three most-attacked industries in all six geographic regions. Manufacturing followed, appearing in five of the six regions. No other sector appeared more than twice.
 Particular Passwords
Particular Passwords
25 passwords accounted for 33% of all authentication attempts against NTT Security Honeypots.
 DDoS Attacks in Asia and Australia
DDoS Attacks in Asia and Australia
DDoS attacks accounted for less than 6% of all attacks worldwide, but they made up 16% of attacks in Asia and 23% of attacks in Australia.
 Outbound Traffic in the Americas
Outbound Traffic in the Americas
Companies in the Americas accounted for 99% of outbound peer-to-peer traffic and included the applications BitTorrent, Hola VPN and Groove Virtual Office.
 Recommendation: Update and Patch
Recommendation: Update and Patch
Keep all devices updated. Without updates and patches, devices may be insecure, and attackers can take advantage of that.
 Recommendation: Prepare and Educate
Recommendation: Prepare and Educate
Prepare for phishing attacks and educate employees. Sent through emails, text and phone calls, these attacks try to trick people into clicking on phony websites or providing information to impersonators.
 Recommendation: Manage Passwords
Recommendation: Manage Passwords
Use a strong, unique password for each account. Remembering all of them is virtually impossible, but password manager utilities or other automated aids can store them securely.